The following guidance material is intended to assist aged care services to implement and maintain compliance with the Quality Standards. 1 administer a symptom screen and the test routinely used in the setting ie TST or BAMT to persons who previously had negative results.
It describes the intent of the Standards and the Commissions expectations of performance and provides supporting information and examples of evidence of compliance.
. Best available This refers to a group of writers who are good at academic writing have great writing skills but are new in our team of writers. Gram-negative bacillary sepsis with shock has a mortality rate of 12 to 38 percent. We have encrypted all our databases.
A researcher creates an antibiotic that binds to a protein present only on B. Wishing for a unique insight into a subject matter for your subsequent individual research. A superinfection is caused by.
Seki M Machida H Yamagishi Y Yoshida H Tomono K. We provide solutions to students. 2 if the initial result is negative the test and symptom screen should be repeated 810 weeks.
The rise in antimicrobial resistance over the past decades has led to the increasing challenge of urinary tract infections because of multidrug-resistant and difficult-to-treat resistance among Gram-negative. After a couple of years using this antibiotic some resistant organisms are found. Which of the following best explains how scientists are able to introduce the bacterial gene for Bt toxin into the cotton plant genome.
The following steps should be taken in a setting that uses TST or BAMT to screen for M. These organisms pose serious therapeutic problems because of the increasing incidence of multidrug resistance. Mortality varies depending in part on whether the patient receives timely and appropriate antibiotic therapy 2-4.
Nosocomial outbreak of multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa caused by damaged transesophageal echocardiogram probe used in cardiovascular surgical operations. Which of the following best outlines the mechanism for development of this resistance. Stenotrophomonas Xanthomonas maltophilia is a multidrug-resistant gram-negative bacillus that is an opportunistic pathogen particularly among hospitalized patients.
This means they recently joined the team. Maltophilia infections have been associated with high morbidity and mortality in severely immunocompromised and debilitated individuals. There has been a dramatic rise in antibiotic-resistant strains including.
MDROs make certain HAIs more difficult to treat. Please Use Our Service If Youre. Although resident micro-flora on the skin include bacteria viruses and many types of fungi we will limit and focus the discussion by concentrating specifically on bacteria.
J Infect Chemother 2013. Place the various organisms in order from most resistant to least resistant to antimicrobial agents. This phenomenon occurs when an individual takes an antibiotic for a long time or when an individual takes an antibiotic that is not necessary.
The following are some of the ways we employ to ensure customer confidentiality. Anthracis the causative agent of anthrax lysing the cell from the outside. Urinary tract infections including cystitis acute pyelonephritis and prostatitis are among the most common diagnoses prompting antibiotic prescribing.
Multidrug-resistant organisms MDROs are bacteria or other organisms that are resistant to more than one antibiotic. In the following review we focus on literature that describes the skin microbial flora.

Supplemental Materials For Multidrug Resistant Bacterial Infections In Patients With Decompensated Cirrhosis And With Acute On Chronic Liver Failure In Europe Journal Of Hepatology

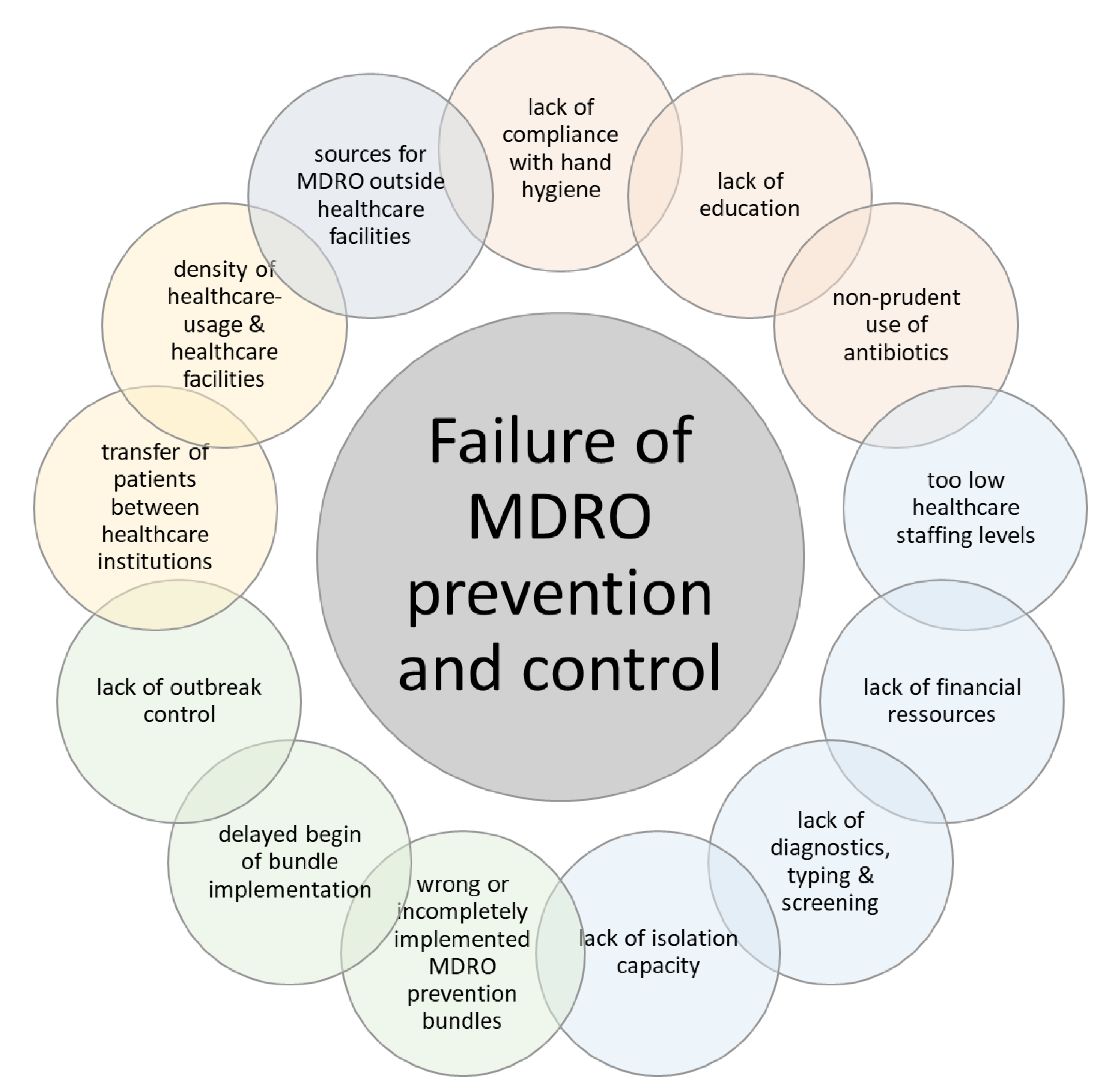
Ijerph Free Full Text Prevention And Control Of Multidrug Resistant Bacteria In The Netherlands And Germany The Impact Of Healthcare Structures Html


0 Comments